
In some areas of the world, anything less than real-time reaction can put lives at stake.
When a military ground vehicle carrying troops through territorial conflict is targeted by airborne explosive devices, its threat mitigation system detects and neutralizes the oncoming bomb. Passengers within the ground vehicle remain unharmed as it continues on its way.
This lightning-fast response is enabled by a deterministic Ethernet networking solution developed by DornerWorks. The same Audio Video Bridging IP has also been applied to blast mitigation and laser warning systems.

Systems that rely on data being sent over a network as quickly and as efficiently as possible have typically been categorized as Forwarding and Queuing of Time-Sensitive Streams (FQTSS) systems defined in IEEE 802.1Q-2014. But FQTSS leaves room for improvement in three main areas:
The patented AVB IP from DornerWorks is a solution to these problems.
Logic-based IEEE 802.1Q Packet Transmission Scheduling enables high-efficiency gapless scheduling of packet transmission in a MAC using a logic circuit. It features an integrated and highly accurate gPTP module with 8ns accuracy and credit-based and strict-priority scheduling for FPGAs.
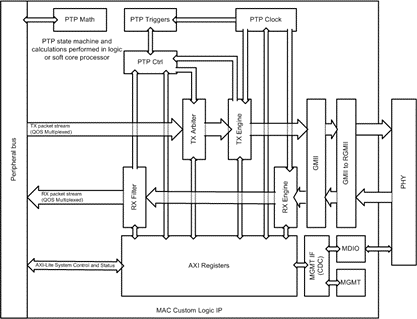
The AVB IP consists of a logic circuit that implements a TX arbiter for an endpoint that combines both credit-based and strict-priority schedulers. This enables gapless scheduling between different qualities of service (QoS) which would otherwise be sent with space between resulting in lower bandwidth.
“There’s always a tradeoff between deterministic traffic and bandwidth,” says DornerWorks FPGA engineer Dave VerBree. “Whenever you try to reserve bandwidth, you’re using it even if you’re not sending data. We’re basically trying to reduce the amount of overhead required when reserve bandwidth. The gaps between packets when we switch between high and low priority queues have been eliminated so there’s effectively no overhead to our traffic scheduling.”
The TX arbiter provides backpressure to the producer, so it is always aware of exactly when the stream is actively being transmitted. This is an alternative to buffering packets in the MAC, which increases variance in a system’s latency. Custom buffers can be added by the customer if needed.
The AVB IP currently provides a reliable networking foundation for threat-mitigation systems protecting the lives of US Army troops. It also has potential in many products outside of defense applications, anywhere determinism and real-time control is required. For example, flight or train control and industrial applications can benefit from the increased bandwidth and synchronization enabled by real-time Ethernet networks. The opportunity to use the same network for multiple classes of information can help reduce system costs, as well.
DornerWorks engineers developed this AVB IP system and methodology to help companies change the world with their own time-sensitive systems. We can help you implement it in your Ethernet networked products, too. Schedule a meeting with us today and turn your ideas into reality.